What are code issues?
When a system is expected to behave in a certain way and it fails to meet the result, the issue occurs. Similarly, any defect or bug found in the code leads to code issues. BrowserStack Code Quality helps to identify the code issues in your software and provide the solutions for the same.
There are different languages in which these code checks are written.
Vulnerabilities
The software vulnerability is basically an error or a weakness present in the software code. Those are product-related threats that can hamper your data and gain access to your products and data.
Once, a vulnerability is detected in a code, there is a high risk from a security perspective. External attackers can exploit and trigger the information systems. This may affect the performance of your product.
Vulnerabilities can be caused due to many reasons like design implementation, input validation errors, code injection, complexity in building large systems, and so on.
The most effective way to prevent these vulnerabilities is by enforcing standard security practices. Check here to know more about security standards supported by BrowserStack Code Quality.
Supported languages
To explore all vulnerabilities categorized by language, visit this link.
Code checker configuration
Code checker configuration helps you to enable or disable code checkers and their corresponding rules for any repository.
Steps to navigate to code checker configuration
- Select the Code checkers configuration option from the repository context menu of the desired repository.
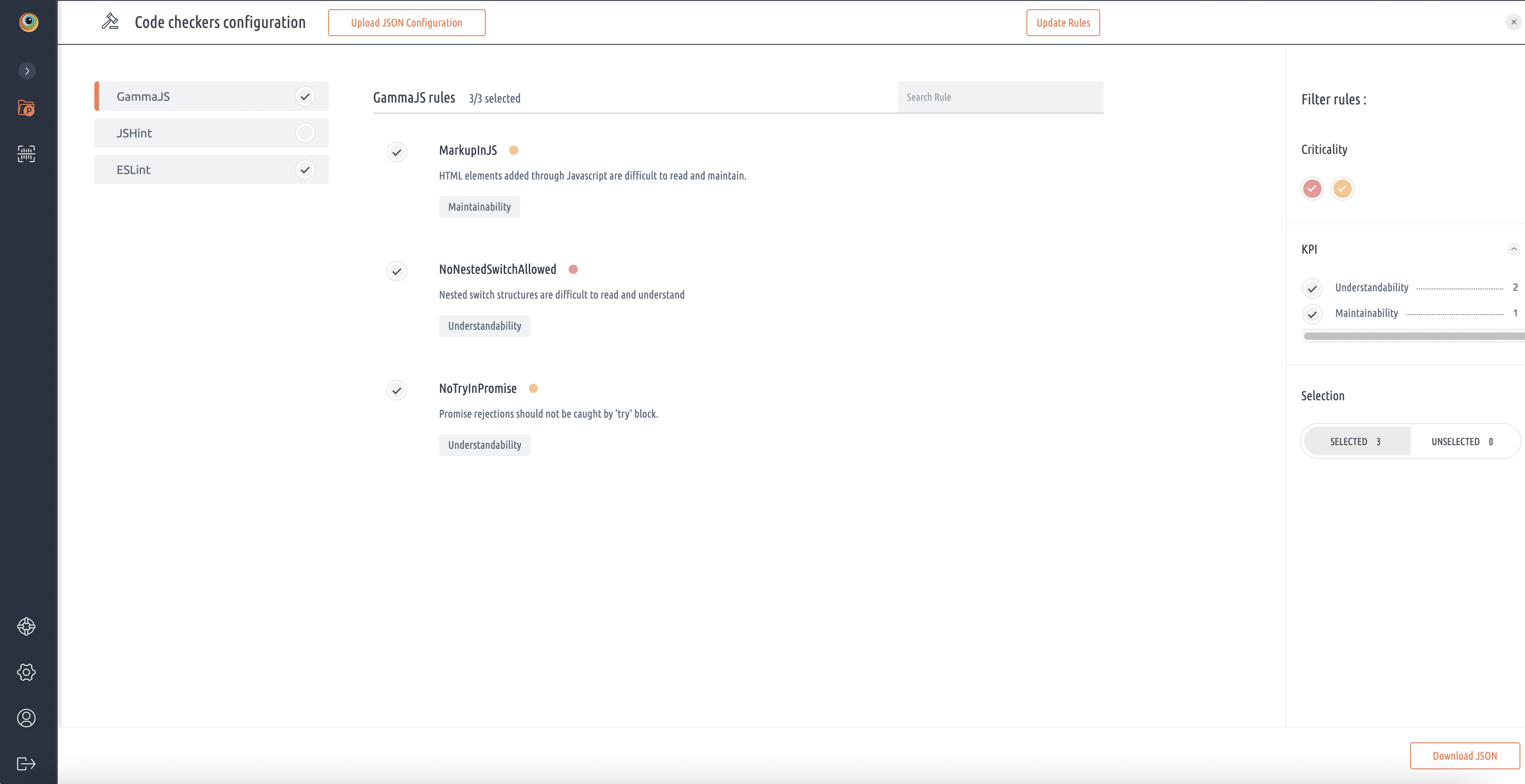
- On the Code checkers configuration page, on the left side navigation pane, by default, code issues are enabled except few.
- Check or uncheck the radio button to enable or disable a specific rule. If you want the checkers to be disabled, you can disable the code checkers (for example GammaCXX or cppcheck).
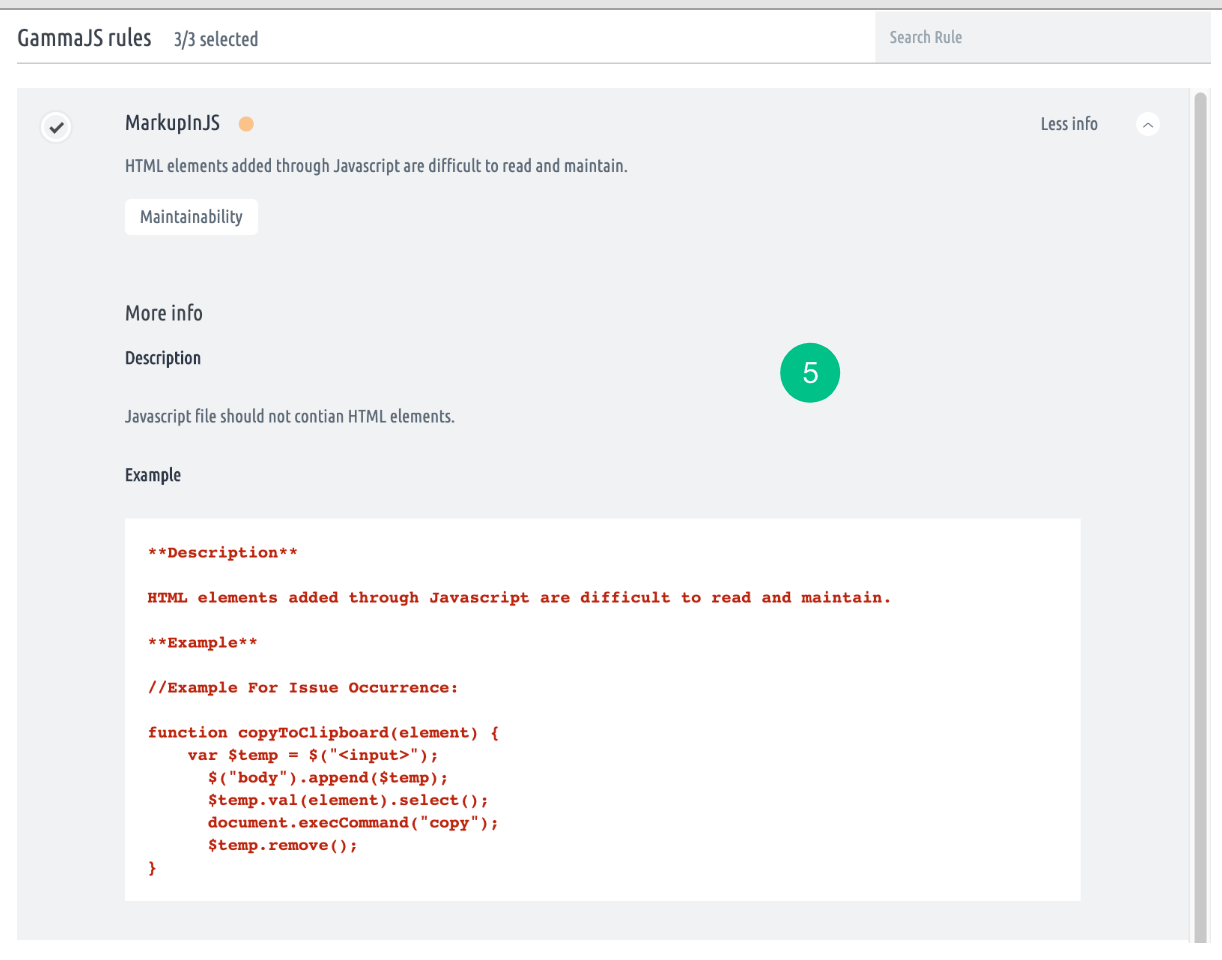
- For a specific selected checker, rules will be displayed.
- Move the cursor on the desired rule to view the More info button. More info will display a detailed description and examples.
- Users can search rules manually by typing in the search text box.
- On the right side navigation pane, the Filter Rules section can be used to filter the displayed rules based on Criticality or by associated KPI.
- To download the file, click Download JSON at the bottom right corner of the code configuration page. This file provides a customized configuration in JSON format and you can change it manually.
- To upload the changed file, click Upload JSON Configuration at the top of the code configuration page.
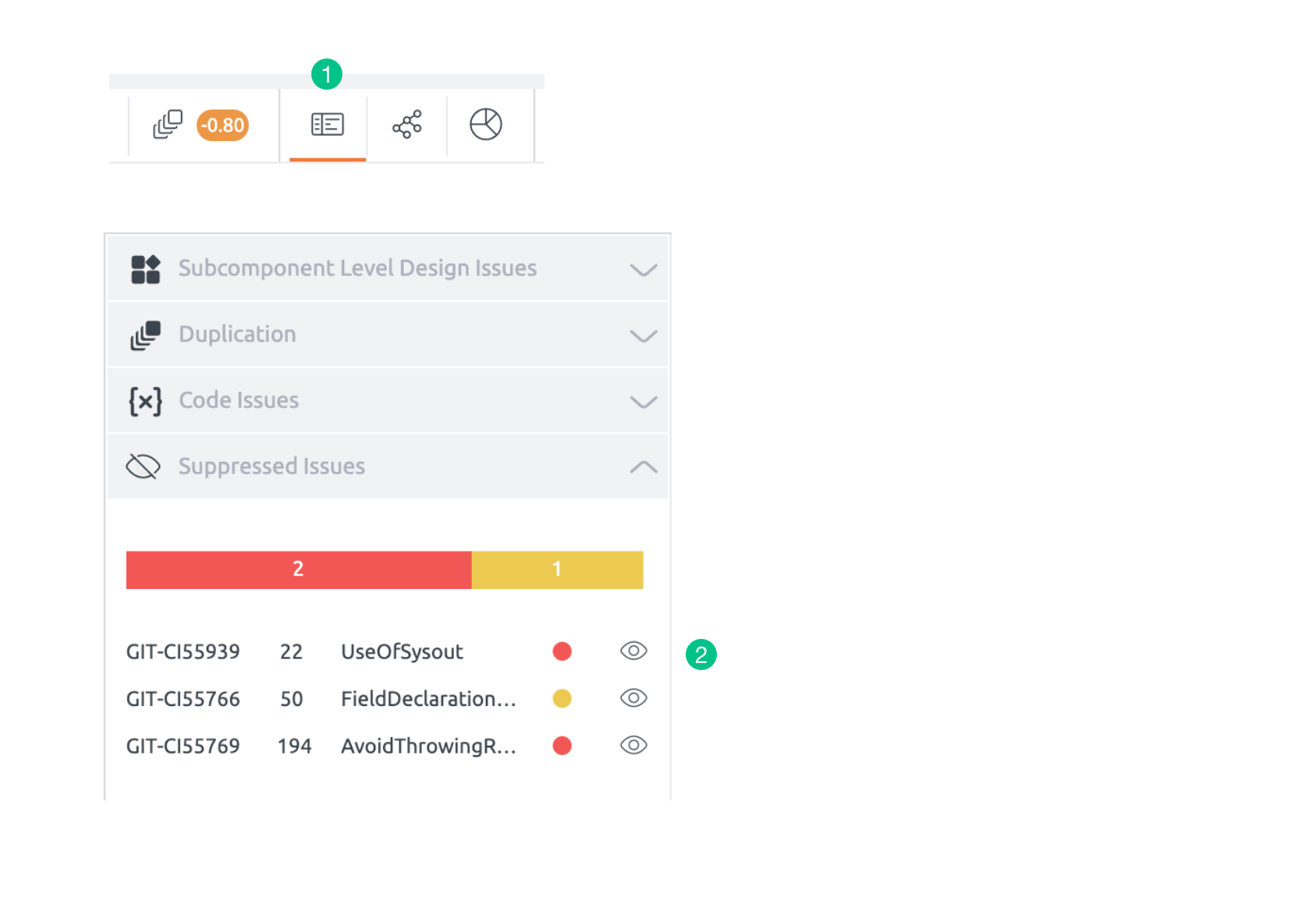
Issue Suppression
Code issues are one of the important assets of BrowserStack Code Quality analysis. Issue suppression is a feature that lists the suppressed code issues within a file/project. Suppression means basically ignoring some parts or a whole parts of the code.
In a few cases, code analysis gives false-positive. Issue suppression is a feature that allows users to suppress these false-positive issue occurrences. This is important because disabling the issue type entirely will not be correct in many cases. If one issue is suppressed, it will be taken off from the code issues panel and will be moved to separate suppressed issues panel.
Steps for suppressing an issue:
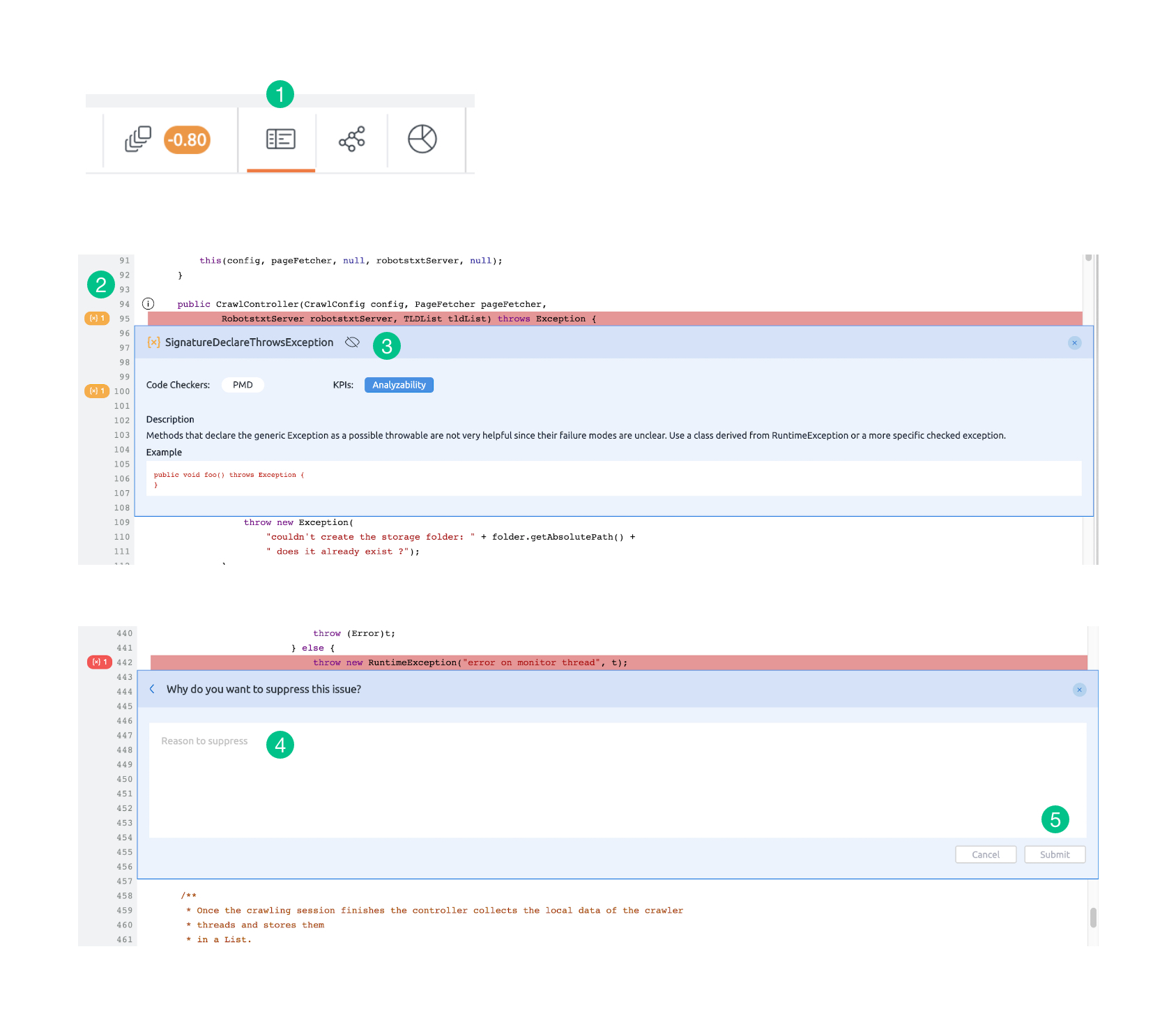
1. Go to the Component Explorer present at the top navigation bar next to the duplication tab.
2. Click on the icon on the left side for the issue to be suppressed.
3. Click on “Suppress this occurrence” icon.
4. Add comment i.e. the reason for suppression.
5. Click on the Submit button.
Steps for unsuppressing an issue :
- Go to the Component Explorer present at the top navigation bar next to the duplication tab.
- From the Suppressed Issues tab, click on the unsuppress icon.
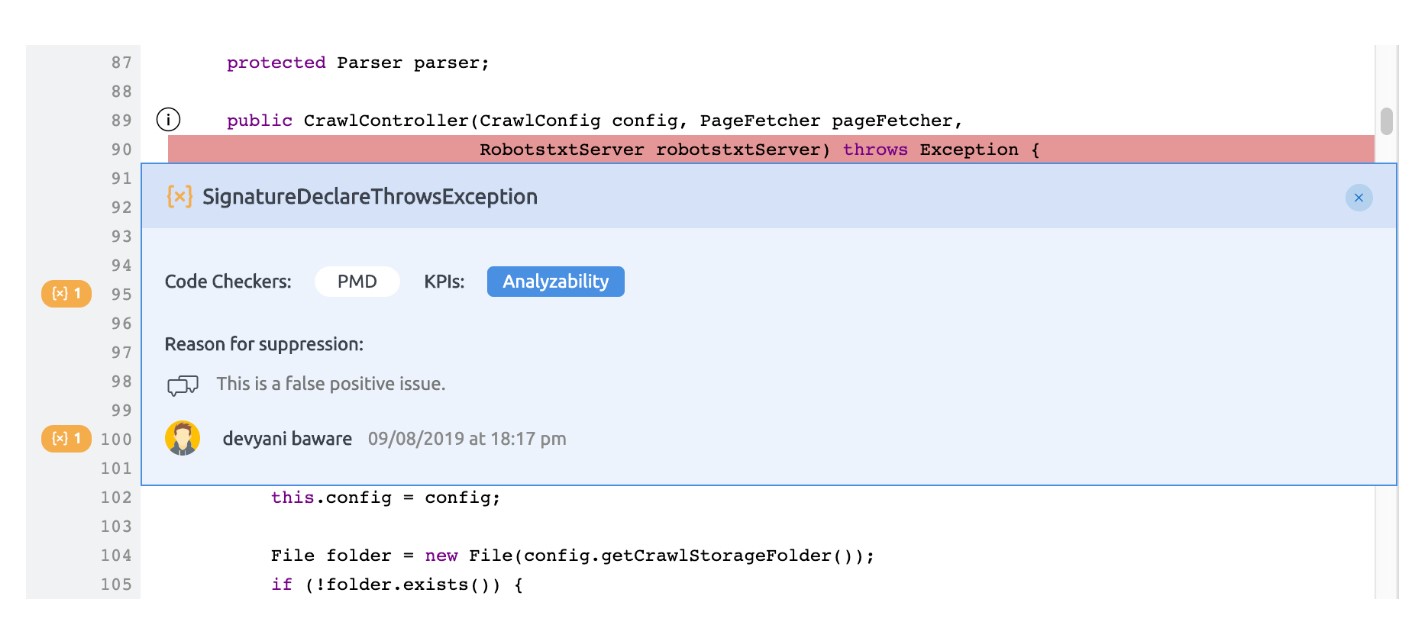
Suppression details can be seen on click of suppressed issue .
Suppression Review Workflow
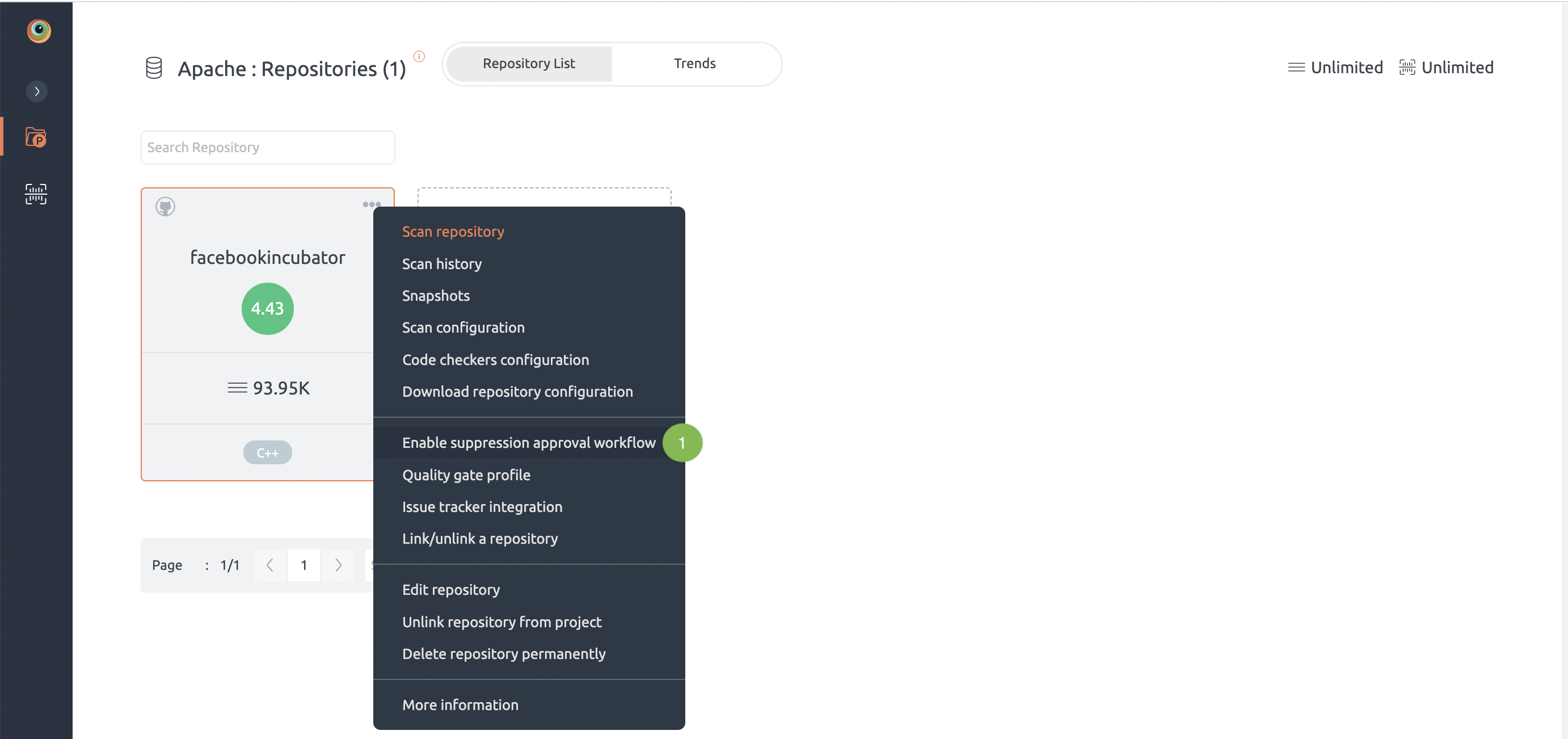
This feature is only available for enterprise customers.
- Select three dots on repository’s page and click on enable suppression approval work flow.
2. When a developer suppresses an issue, project manager, project admins and super admins will see the list of suppressed issues on newly introduced Suppression Status page.
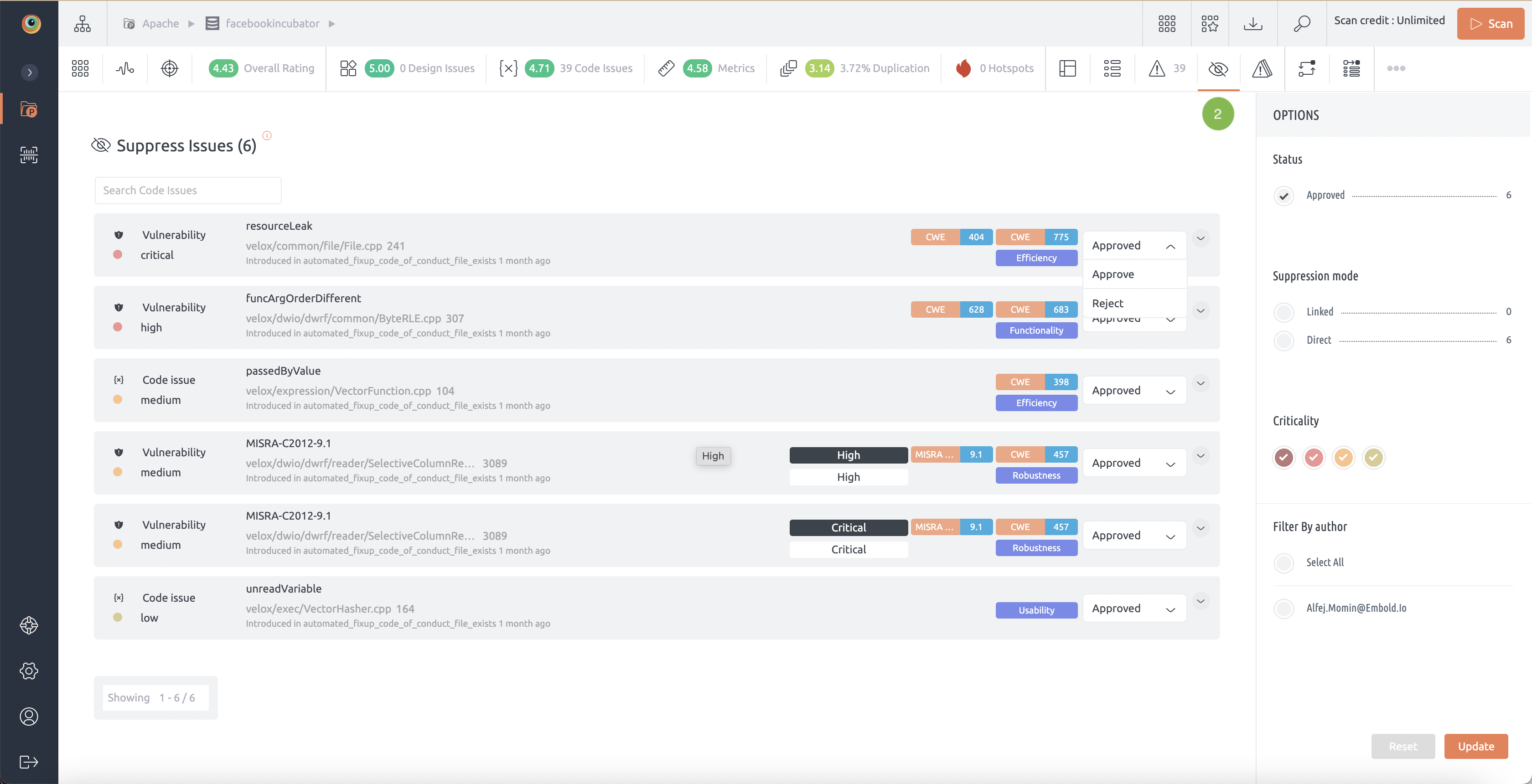
3. Project manager, project admins and super admins can review – Accept or Reject suppressions.
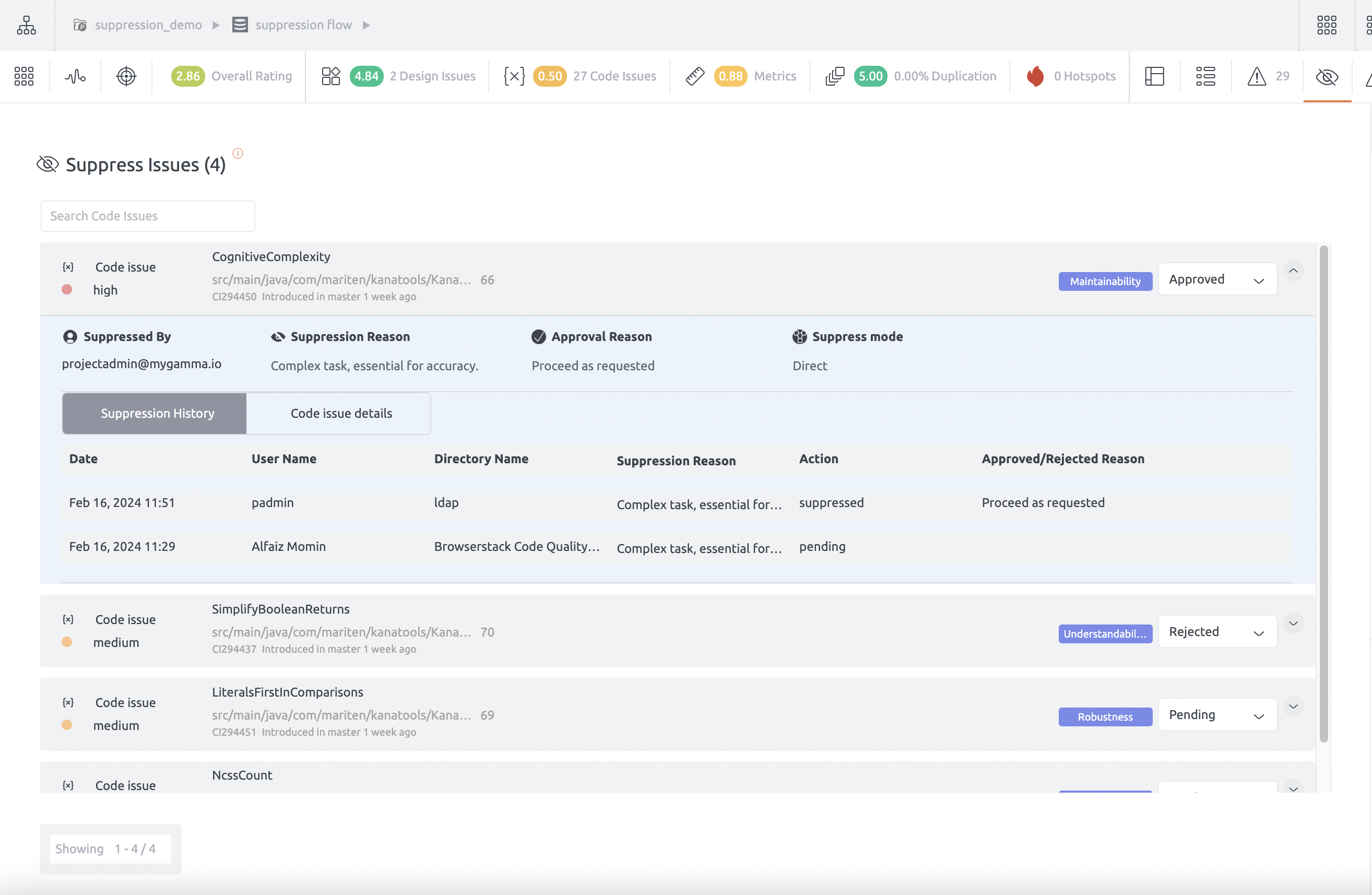
Suppression history
The suppression history feature allows users to view a comprehensive log of suppression actions taken on certain issues. This log includes details such as the name of the user who initiated the action, the reason for the suppression, the status of the suppression (whether it was pending, approved or rejected), any accompanying reasons for approval or rejection, and the date on which the action occurred. This feature provides transparency and accountability regarding the management of suppression issues within the system.
See screenshot below for reference
Generic module
The generic module is used to import code issues from a csv file. Regardless of language or combination of languages, if you get your code issues data into the generic format(CSV) as specified by this module, it will be imported and correctly applied.
Module Name:
gamma_generic
The supported format(CSV) looks like:
| File | Line | Severity | Description | Rule | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| src/main/java/com/mariten/kanatools/KanaConverter.java | 26 | Low | This issue is having low criticality. | Custom Rule | CWE=146;MISRA=444;CWE=123 |
| src/main/java/com/mariten/kanatools/KanaConverter.java | 33 | High | This issue is having High criticality. | Rule-01 | Tag1 |
| src/main/java/com/mariten/kanatools/KanaConverter.java | 45 | low | This issue is having low criticality. | custom Rule 3 | CWE=231;CWE=867 |
| src/main/java/com/mariten/kanatools/KanaConverter.java | 25 | Medium | This issue is having medium criticality. | custom Rule-04 | CWE=453 |
| src/main/java/com/mariten/kanatools/KanaConverter.java | 39 | Medium | This issue is having medium criticality. | custom Rule 5 | NewTag;TagTest1 |
| src/main/java/com/mariten/kanatools/KanaConverter.java | 43 | Critical | Critical | custome Rule 8 | NewTag;TagTest1;Tag_123 |
Supported severity types :
Critical, High, Medium, Low and Info
Supported input tag formats :
only tag name: tag1
multiple tag with only name: tag2;tag3
name and value: CWE=330
multiple tag with name and value: CWE=330;CWE=200
Usage
Run a remote scan.
- Any CSV file name will work

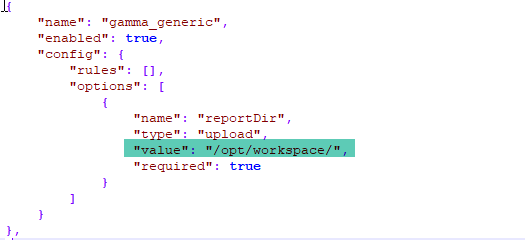
2. By Providing CSV PATH relative to base directory
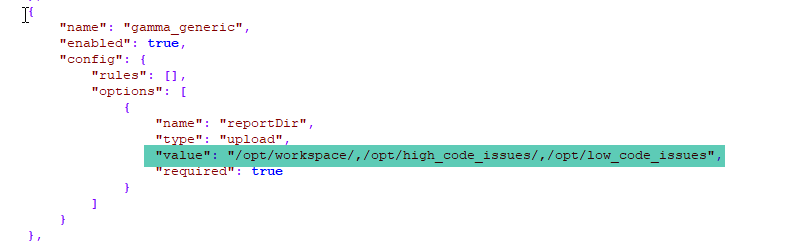
3. In a remote scan, multiple CSV files can be given with comma-separated paths
For more information regarding RemoteScan, please click here.
