Brain Class is a class that is complex partly because it implements a significant amount of system intelligence and partly because it holds one or more Brain methods.
Impact
- Low cohesion impacts understandability, maintainability and testability.
- Since a Brain Class becomes less cohesive or non-cohesive, refactoring becomes painful. Moreover, refactoring of Brain methods which are large and complex becomes even more complicated.
Characteristics
- The class is very large and complex (high LOC and has complex methods).
- The class has either:
- One Brain method and size of all methods is very large, Or,
- Has more than one Brain Methods, and methods are large and functional complexity is very high.
- The class is non-cohesive.
- The class is not a God class because it does “not” access foreign data significantly.
Example(s)
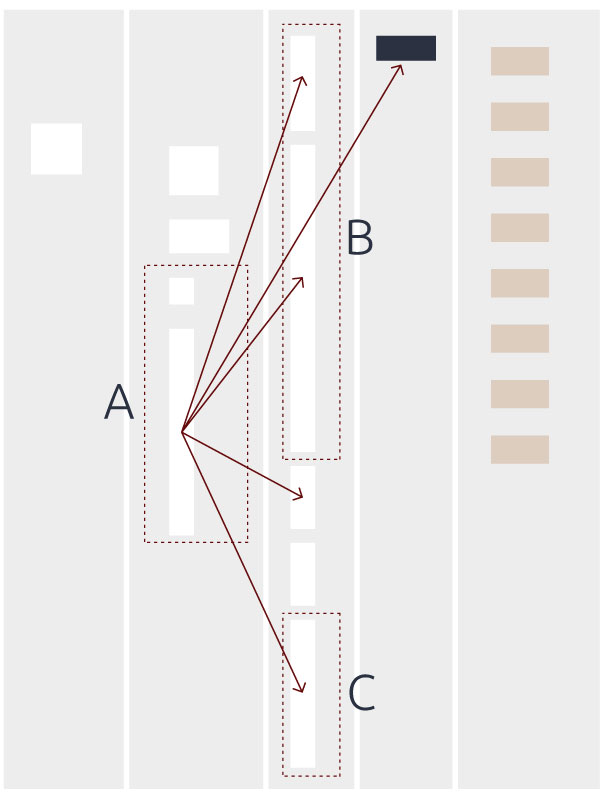
Analysis of class TokenMaker indicates:
- TokenMaker has 14 methods and 12 attributes.
- A Brain Method: A represents public method markTokens( )
- B Brain Method: B represents private method
handleRule ( ) - C Brain Method: C represents private method markKeyword( )
- Additionally: A, B,
and C methods are represented as lengthy blocks indicating that their individual number of lines of code is significantly high.
Guidelines
- Split a
non cohesive class into two or more cohesive classes. Follow the ‘one class one task’ rule. - When creating class methods, avoid creating large and complex methods.
- Try refactoring Brain methods by splitting them into multiple methods (refer to guidelines of ‘Brain Method’ on how to split Brain methods).
- Brain methods tend to use significant duplicate code. Extract duplicate code into separate methods.
- Brain methods are often a result of incremental additions of functionality to existing methods. When adding new code to an existing method, keep LOC within
limit . If not, create a new method - In some
cases a Brain class may be harmless, especially if proved over time that it has had no maintenance problems and is stable. In such a case avoid the costly effort of refactoring such a class.
